Purinergic signaling mediates neuroglial interactions to modulate sighs
Por um escritor misterioso

Sighs prevent the collapse of alveoli in the lungs, initiate arousal under hypoxic conditions, and are an expression of sadness and relief. Sighs are periodically superimposed on normal breaths, known as eupnea. Implicated in the generation of these rhythmic behaviors is the preBötzinger complex (preBötC). Our experimental evidence suggests that purinergic signaling is necessary to generate spontaneous and hypoxia-induced sighs in a mouse model. Our results demonstrate that driving calcium increases in astrocytes through pharmacological methods robustly increases sigh, but not eupnea, frequency. Calcium imaging of preBötC slices corroborates this finding with an increase in astrocytic calcium upon application of sigh modulators, increasing intracellular calcium through g-protein signaling. Moreover, photo-activation of preBötC astrocytes is sufficient to elicit sigh activity, and this response is blocked with purinergic antagonists. We conclude that sighs are modulated through neuron-glia coupling in the preBötC network, where the distinct modulatory responses of neurons and glia allow for both rhythms to be independently regulated. Sighs are augmented breaths necessary to maintain normal breathing. Here, the authors show that sighs are generated within the preBötzinger complex by emergent network properties that involve neuroglial interactions mediated by purinergic signaling as well as intrinsic and extrinsic modulatory inputs.
Sighs prevent the collapse of alveoli in the lungs, initiate arousal under hypoxic conditions, and are an expression of sadness and relief. Sighs are periodically superimposed on normal breaths, known as eupnea. Implicated in the generation of these rhythmic behaviors is the preBötzinger complex (preBötC). Our experimental evidence suggests that purinergic signaling is necessary to generate spontaneous and hypoxia-induced sighs in a mouse model. Our results demonstrate that driving calcium increases in astrocytes through pharmacological methods robustly increases sigh, but not eupnea, frequency. Calcium imaging of preBötC slices corroborates this finding with an increase in astrocytic calcium upon application of sigh modulators, increasing intracellular calcium through g-protein signaling. Moreover, photo-activation of preBötC astrocytes is sufficient to elicit sigh activity, and this response is blocked with purinergic antagonists. We conclude that sighs are modulated through neuron-glia coupling in the preBötC network, where the distinct modulatory responses of neurons and glia allow for both rhythms to be independently regulated. Sighs are augmented breaths necessary to maintain normal breathing. Here, the authors show that sighs are generated within the preBötzinger complex by emergent network properties that involve neuroglial interactions mediated by purinergic signaling as well as intrinsic and extrinsic modulatory inputs.

The hypoxic respiratory response of the pre-Bötzinger complex - ScienceDirect

Purinergic neurone-glia signalling in cognitive-related pathologies - ScienceDirect
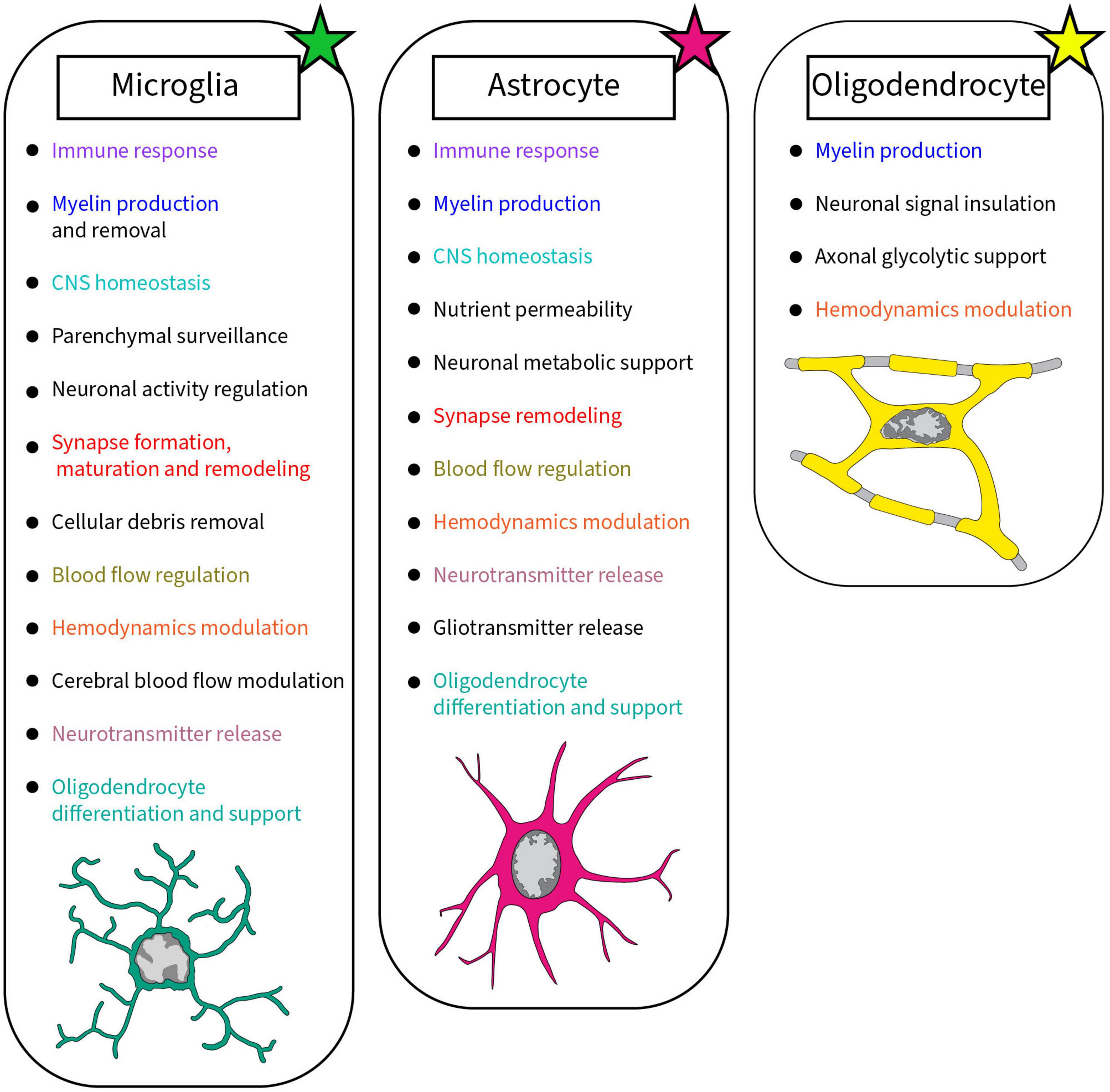
Frontiers The implication of a diversity of non-neuronal cells in disorders affecting brain networks

Microglia-induced neuroinflammation in hippocampal neurogenesis following traumatic brain injury: Heliyon
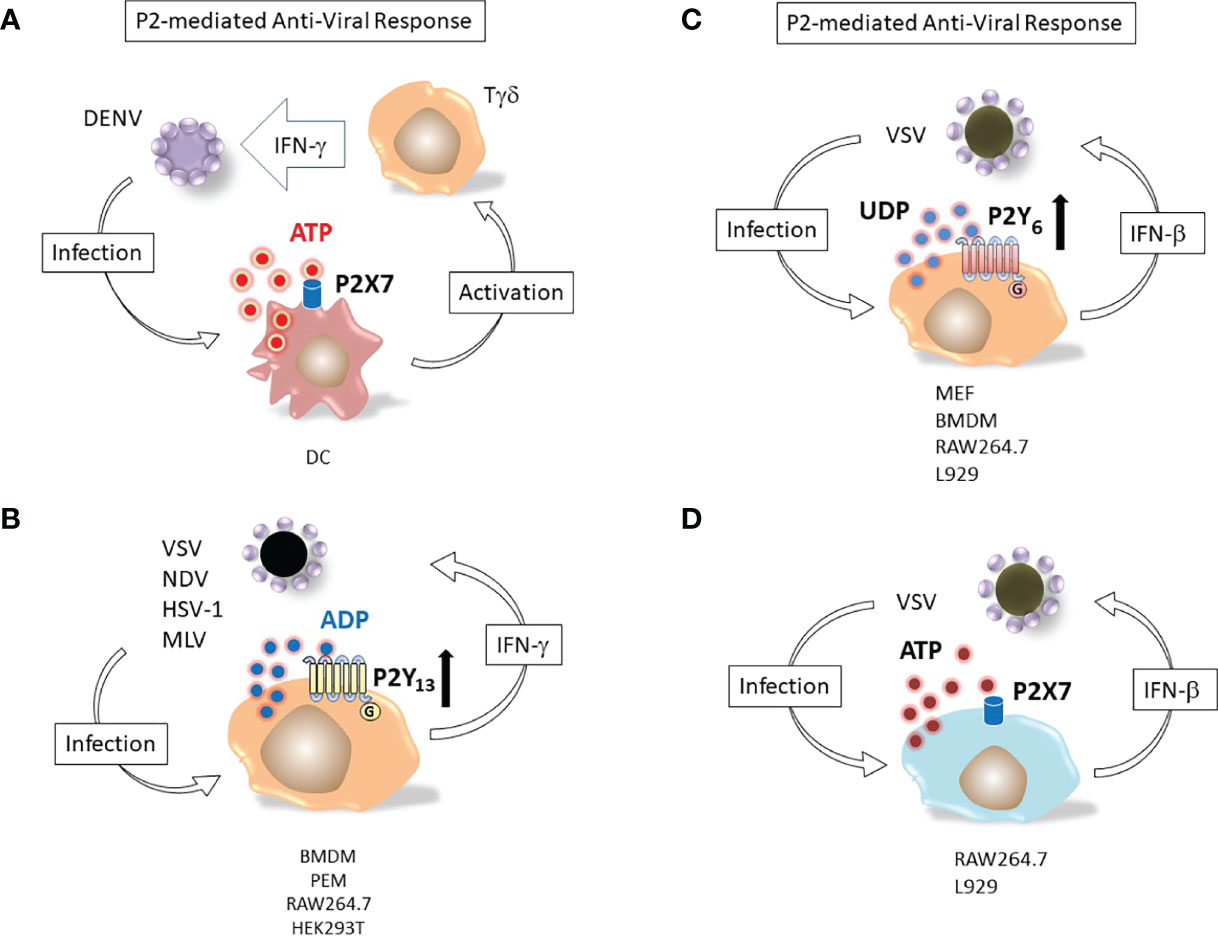
Frontiers The Potential of Purinergic Signaling to Thwart Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2

Modulation of axon growth by purinergic receptors. (A) Schematic
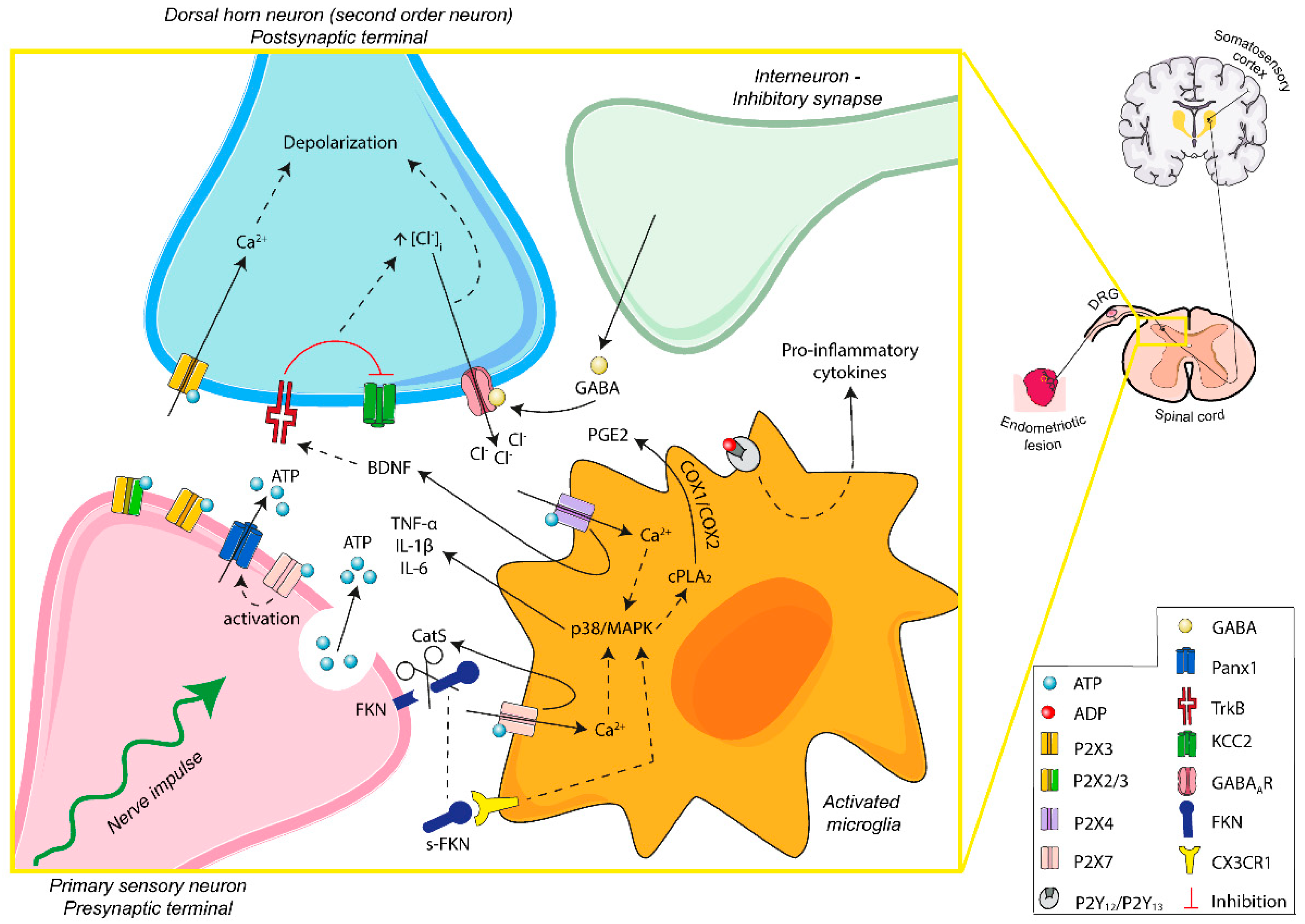
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Purinergic signalling: From normal behaviour to pathological brain function - ScienceDirect

Local neuronal activation evokes ictal discharges. (A) Drawing and

Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system

Neuroglia and their roles in central respiratory control; an overview.

Autonomously active neurons are part of the spectrum of intrinsic